
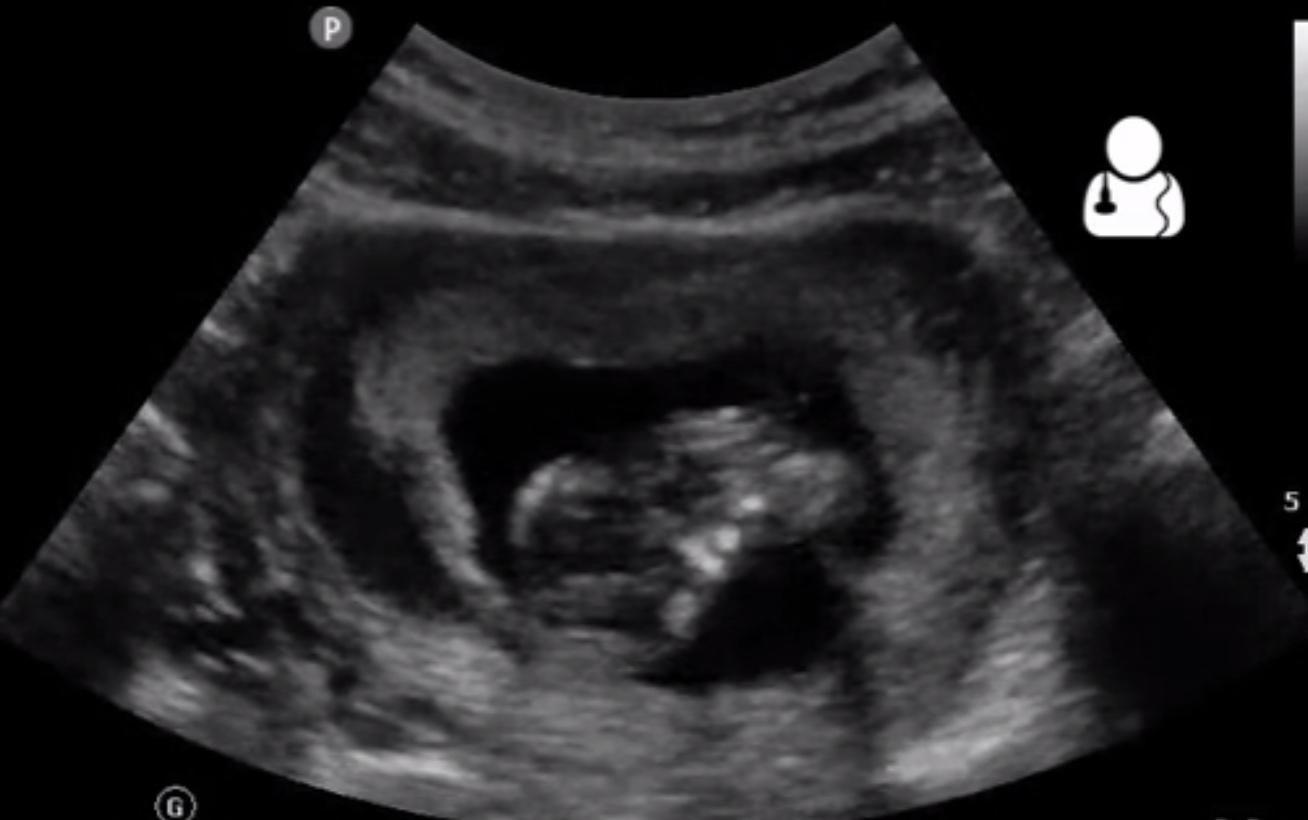
Placental lakes or intervillous spaces are usually hypoechoic with swirling echoes and demonstrate low-velocity laminar flow at B-mode or Doppler imaging. Lakes in the placenta are one of the best predictive signs in diagnosis of placenta accreta in the third trimester 16.
However it is always recommended to seek medical consultation in case it is visible in the ultrasound.
Placental lakes third trimester. Target ultrasonography for diagnosis of placental lake was performed in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy and followed up in the 3rd trimester. Placental lakes were defined as homogenous sonolucent avillous lesions greater than 2 cm 2 cm in diameter. The 109 pregnant women enrolled in this study were divided into four groups according to the size and change in size of placental lakes.
Some of the mothers may experience one placental lake and on the same time the other can have even three venous lakes during her third trimester. Though having placental lakes is nothing much serious and there will be no problem to the baby or birthing process one must go to the doctor and take medical advice if it is noticed in scans. The other placental lakes persisted in the 3rd trimester but there were no cases in which the size of lake increased.
Pregnant women with a large placental lake had only one lake. In the small placental lake cases there were some patients with two or three small lakes but there was no correlation between the number of placental lakes and adverse pregnancy outcome data not shown. Placental lakes can occur in any pregnancy and the feature can be easily detected during an ultrasound.
In general their presence has not been associated with complications or adverse pregnancy outcomes. So do not worry if your placenta has a placental lake. Eat well rest well and get your regular check-ups to have a healthy pregnancy.
It is not one a woman who can experience this can detect one or even three or more placental lakes in ultrasound in the last trimester. This also has no negative effects on the baby or the birthing process. However it is always recommended to seek medical consultation in case it is visible in the ultrasound.
By now it is clear that it is a commonplace phenomenon and not something to dread. Placental venous lakes refer to a phenomenon of formation of hypoechoic cystic spaces centrally within the placenta. Finding placental lakes during a second trimester ultrasound scan is not associated with any uteroplacental complication or with an adverse pregnancy outcome.
They can however be abnormal if very diffuse or if seen very early in pregnancy. For example in the third trimester placental lakes in a Grannum classification Grade 3 placenta are considered normal when accompanied by calcifications and indentations in the chorionic plate. In ultrasound examinations the presence of placental lakes or vesicules may suggest a number of different pathologies.
At discovery placental lakes must not be confused. Placental lakes can be seen within the placenta or on the fetal surface of the placenta bulging into the amniotic cavity. Slow swirling blood flow larger arrow may be seen within the spaces and the shape of the spaces tends to change with uterine contractions.
These features may help to distinguish a placental lakes from a thrombus. A finding of placental lakes was six times more likely with a thick placenta 3 cm at 20 weeks gestation OR 630 95 per cent CI 439 to 905. A finding of placental lakes during the second trimester ultrasound scan does not appear to be associated with uteroplacental complications or an adverse pregnancy outcome.
The lesions are more. Placental lakes or intervillous spaces are usually hypoechoic with swirling echoes and demonstrate low-velocity laminar flow at B-mode or Doppler imaging. They are usually seen in the late second trimester or third trimester.
They are not associated with uteroplacental complications or. Target ultrasonography for diagnosis of placental lake was performed in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy and followed up in the 3rd trimester. Placental lakes were defined as homogenous sonolucent.
Target ultrasonography for diagnosis of placental lake was performed in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy and followed up in the 3rd trimester. Placental lakes were defined as homogenous sonolucent avillous lesions greater than 2 cm 2 cm in diameter. Regarding this what causes a placental Lake.
Placental lakes are enlarged spaces in the placenta filled with maternal blood. In the second and third trimesters placental lakes may be associated with two things. Most important of these the lakes along with other findings may be associated with invasive placental disease.
Other placental disorders third trimester. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 BillableSpecific Code Maternity Dx 12-55 years 3rd Trimester 28 weeks O43893 is a billablespecific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM O43893 became effective on October 1 2020.
Placental lakes happen in about two per cent of pregnancies and are more common when the placenta is thicker than usual. As worrying as this may sound almost all placentas have one or more lakes by the third trimester and it shouldnt affect your baby. Most ultrasound doctors dont report or even mention placental lakes to mums-to-be.
Uteroplacental insufficiency is a common cause of intrauterine growth retardation in the third trimester of pregnancy. Placental infarction third trimester 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 BillableSpecific Code Maternity Dx 12-55 years 3rd Trimester 28 weeks O43813 is a billablespecific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM O43813 became effective on October 1 2020.
Lakes in the placenta are one of the best predictive signs in diagnosis of placenta accreta in the third trimester 16. Interestingly in the first trimester only three of our cases showed placental lakes. Case 5 was the only case with large placental lakes around the cord insertion site that became velamentous at the 20week scan.