
They can however be abnormal if very diffuse or if seen very early in pregnancy. These spaces are also called intervillous spaces because they are found between the placental villi the finger-like projections of the placenta that contain fetal blood vessels.
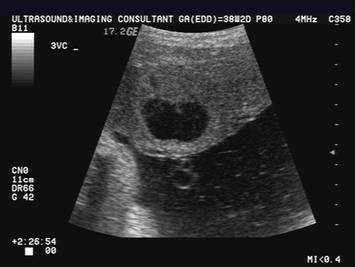
Presence of more than three placental lakes.
Placental lakes second trimester. Placental venous lakes refer to a phenomenon of formation of hypoechoic cystic spaces centrally within the placenta. Finding placental lakes during a second trimester ultrasound scan is not associated with any uteroplacental complication or with an adverse pregnancy outcome. They can however be abnormal if very diffuse or if seen very early in pregnancy.
Placental lakes can be of concern in the following situations 4 7. They occur early in the first trimester or early second trimester. Presence of more than three placental lakes.
The diameter is more than two centimeters. Large placental lakes with a diameter greater than five centimeters. A finding of placental lakes was six times more likely with a thick placenta 3 cm at 20 weeks gestation OR 630 95 per cent CI 439 to 905.
A finding of placental lakes during the second trimester ultrasound scan does not appear to be associated with uteroplacental complications or an adverse pregnancy outcome. The lesions are more prevalent with increasing placental thickness. The doctor will keep an eye on the babys development in case of placental lakes in the second trimester since it can lead to a less-than-average fetus size.
However if the placental lake covers more than 10 of the placenta and seems abnormally large there is a. Target ultrasonography for diagnosis of placental lake was performed in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy and followed up in the 3rd trimester. Placental lakes were defined as homogenous sonolucent avillous lesions greater than 2 cm 2 cm in diameter.
The 109 pregnant women enrolled in this study were divided into four groups according to the size and change in size of placental lakes. Doctor pays more attention and keeps the check on the babys development in case of placental lakes in second trimester as it might cause reduction of average foetus size. If the placental lake covers more than 10 of placenta and appears to be abnormally large there is minimal risk of placenta growth accumulation.
Having placental lake is not too worry-some as it does not lead to any negative outcomes of pregnancy but can affect the baby size in case it gets detected in the second semester and this can be controlled as well if the doctor keeps a strict check on the growth of the baby ensuring it does not lag. During early second trimester placental lacunae usually appears as single or multiple irregularly-shaped intraplacental anechoic areas measuring 1 cm. Under that size sonographers will usually speak of a vesicular or multivesicular placenta they are usually more regularly-shaped than placental lacunae.
Placental lakes are enlarged spaces in the placenta filled with maternal blood. These spaces are also called intervillous spaces because they are found between the placental villi the finger-like projections of the placenta that contain fetal blood vessels. Placental lakes or intervillous spaces are usually hypoechoic with swirling echoes and demonstrate low-velocity laminar flow at B-mode or Doppler imaging.
They are usually seen in the late second trimester or third trimester. They are not associated with uteroplacental complications. Target ultrasonography for diagnosis of placental lake was performed in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy and followed up in the 3rd trimester.
Placental lakes were defined as homogenous sonolucent avillous lesions greater than 2 cm 2 cm in diameter. Regarding this what causes a placental Lake. Placental lakes are enlarged spaces in the placenta filled with maternal blood.
Target ultrasonography for diagnosis of placental lake was performed in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy and followed up in the 3rd trimester. Placental lakes were defined as homogenous sonolucent avillous lesions greater than 2 cm 2 cm in diameter. Target ultrasonography for diagnosis of placental lake was performed in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy and followed up in the 3rd trimester.
Placental lakes were defined as homogenous sonolucent. Placental sonolucency elevation of maternal serum AFP and pregnancy outcomes. Singleton pregnancies n 168 with second trimester serum AFP level 20 weight-adjusted multiples of the median MoM were recruited as the study group.
Women with second trimester. A finding of placental lakes during the second trimester ultrasound scan does not appear to be associated with uteroplacental complications or an adverse pregnancy outcome. The lesions are more.
Upper mid lower uterus. Use color Doppler in evaluating placental lesions. Marginal sinus vessels have flow but abruption does not.
Both can present with retroplacental hypoechoic region. Placental lakes often have no discernible flow. Use real time grayscale findings to see swirling flow.
Placental lakes occurred in three of 10 pregnancies and were associated with a hysterectomy in two of the three. When the pregnancy evolved over time so that the bulk of the placental tissue and cord insertion were positioned over the myometrium of the anterior wall of the uterus rather than within the scar defect two of seven cases had a hysterectomy Cases 1 and 9. The laterality of the scar defect.
O43892 is applicable to maternity patients aged 12 - 55 years inclusive. O43892 is applicable to mothers in the second trimester of pregnancy which is defined as between equal to or greater than 14 weeks to less than 28 weeks since the first day of the last menstrual period.