
However several experts and agencies including the World Health Organization WHO suggest that the ideal time would be anywhere between one to three minutes. The iron in the blood increases the newborns iron storage which is vital for healthy brain development.
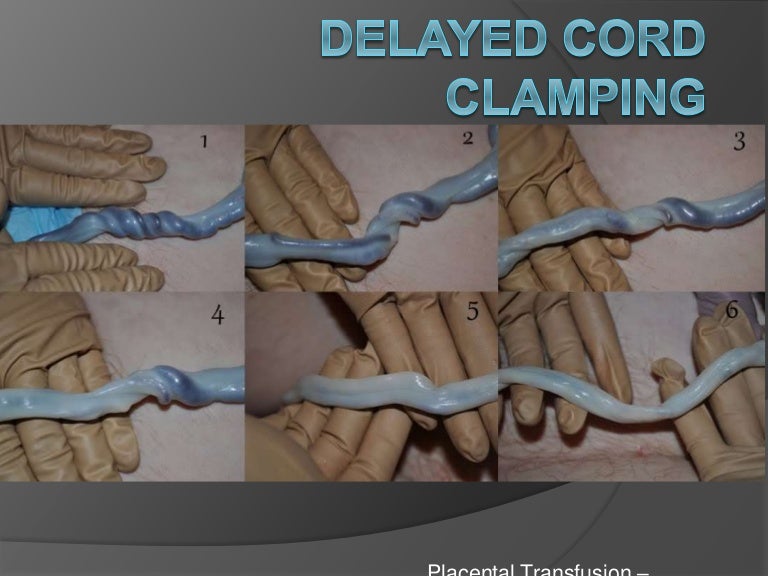
How long to wait Delayed cord-clamping has been gaining increased attention for a while but the precise length of time to wait isnt set in stone.
How long to delay cord clamping. Delayed umbilical cord clamping is usually performed 25 seconds to 5 minutes after giving birth. DCC allows more blood to transfer from the placenta to the baby sometimes increasing the childs blood volume by up to a third. The iron in the blood increases the newborns iron storage which is vital for healthy brain development.
This review defined delayed umbilical cord clamping as a delay of more than 30 seconds with a maximum of 180 seconds and included some studies that also used umbilical cord milking in addition to delayed cord clamping. Delayed umbilical cord clamping was associated with fewer infants requiring transfusion for anemia seven trials 392 infants. Relative risk RR 061.
95 confidence interval CI. How Long Should Cord Clamping be Delayed. It depends who you ask.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists ACOG says at least 30-60 seconds. The World Health Organization recommends at least 1 minute or until the cord has stopped pulsing. How Long Should Cord Clamping Be Delayed.
As mentioned earlier there are no set rules yet as to when an infants cord should be clamped. However several experts and agencies including the World Health Organization WHO suggest that the ideal time would be anywhere between one to three minutes. How long to delay cord clamping.
For healthy newborns the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends a delay of at least 3060 seconds after birth. The World Health Organization recommends a delay in cord clamping of at least one minute. Delayed umbilical cord clamping is the practice of waiting 30 seconds to a few minutes after birth to clamp the umbilical cord.
Delayed cord clamping has benefits for both term and preterm babies. For term babies it boosts iron and antibodies. Delaying one to three minutes before clamping.
The ACOG recommends a delay of at least 30 to 60 seconds for healthy newborns. The standard practice in many US. Hospitals is early clamping so ask.
It depends on who you ask. According to the World Health Organization delayed clamping is when the cord is cut 1-3 minutes after birth a practice they recommend for all births. However some practitioners think the one minute mark is too early and recommend extending the time to.
How long to wait Delayed cord-clamping has been gaining increased attention for a while but the precise length of time to wait isnt set in stone. The World Health Organization currently. NICE guidance recommends that cord clamping is delayed in all maternity units for at least 1-5 minutes in all babies unless the fetal heart is less than 60 bpm and not getting faster at this point for practical reasons the baby may need to be taken away to get breathing support.
Delayed cord clamping is waiting any amount of timefrom 30 seconds to 10 minutesbefore clamping the cord. Most hospitals that practice delayed cord clamping including Texas Childrens Pavilion for Women use a standard cut off of one minute although it can range depending on the situation and patient preferences. But a new scientific review suggests that delaying cord clamping by even one minute increases an infants iron stores for up to six months.
When babies are born they are still attached to their mothers by the umbilical cord which delivers nutrients and oxygen throughout pregnancy. They specifically recommend that the cord clamping be delayed at least one to three minutes. Many women choose to delay cord clamping until the cord actually stops pulsing though.
What exactly is cord clamping. Cord clamping is the process of stopping the blood flow from the placenta to the baby after the baby is born. The World Health Organisation defines the optimal time to clamp your babys cord as when it has stopped pulsating which can be approximately 3 minutes or often much longer after the birth but births and umbilical cords are very individual to each woman and baby.
Delayed Cord clamping simulated during a vaginal and a cesarian birth. Commentary and direction by Becky Bagley RN CNM DNPThis video is property of ECU Col. This study from the New York Blood Center the largest donor bank in the US indicates that delayed cord clamping of 30-60 seconds does not significantly diminish the cell count of cord blood collected for cryopreservation at a public cord blood bank.
Great news for families considering doing both.