Babies have a noticeable rise in blood volume as compared to babies whose cords were clamped and cut off without delay. Delayed clamping means the umbilical cord isnt clamped immediately after birth.
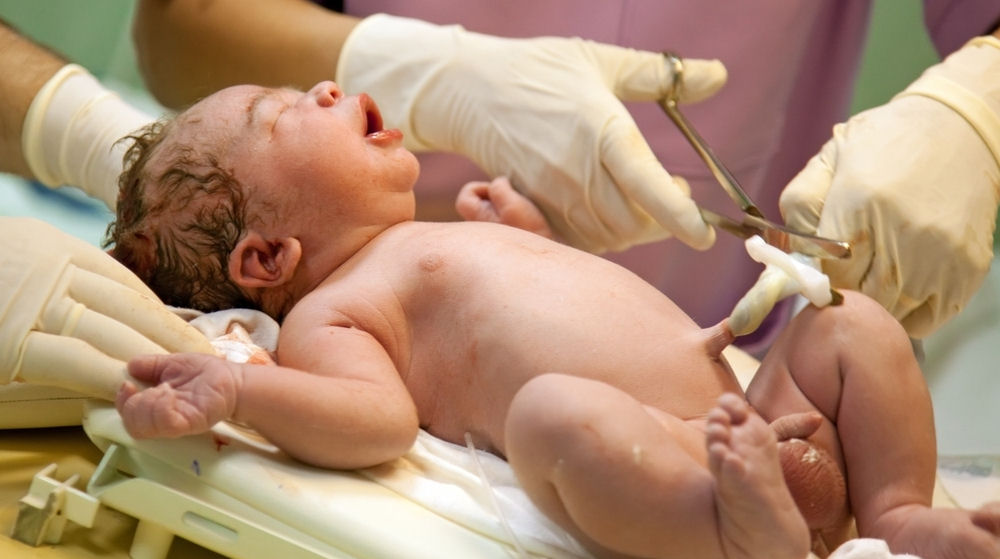
This is called deferred or delayed cord clamping DCC and we advise this for almost all babies.
Delay cutting the umbilical cord. Doctors traditionally cut a newborns umbilical cord right after birth but recent research shows that there may be benefits in delayed cord clamping. Delayed clamping means the umbilical cord isnt clamped immediately after birth. Instead its clamped and cut between one and three minutes after birth.
Currently most hospitals in the United. The guidelines apply to both preterm and full-term births and both vaginal and caesarean deliveries according to the organization. Also both the American College of Gynecologists ACOG and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend a delay in umbilical cord clamping until at least 30 to 60 seconds after birth.
If the placenta is left attached to the umbilical cord and baby after birth for a while it keeps transferring stem cells nutrients antibodies and extr. While before the mid 1950s delayed cord clamping referred to the cutting off the umbilical cord after 5 minutes post delivery the World Health Organization now states that delayed clamping is when the cord is cut 1-3 minutes after birth which is now a standard practice. Because there has not been a specific recommendation for clamping the cord many practitioners choose to clamp the cord as early as 30-60.
And then theres the perspective expressed by the International Childbirth Education Association which is that Delayed cord clamping DCC is a practice by which the umbilical cord is not clamped or cut until after it stops pulsating. It may also include not clamping or cutting the umbilical cord until after the placenta is delivered 3. After birth the babys umbilical cord will be clamped and cut separating the baby from the placenta.
There is evidence that babies benefit from a delay before clamping the cord allowing time for extra blood to flow from the placenta into the baby. This is called deferred or delayed cord clamping DCC and we advise this for almost all babies. Delayed cord clamping is when the umbilical cord is not immediately cut but instead is allowed to pulsate and transfer blood to baby.
As a result billions of red blood cells stem cells white blood cells and other necessary substances from the cord are allowed to pass to the newborn. How Long Should Cord Clamping be Delayed. It depends who you ask.
What is delayed umbilical cord clamping. When a baby is born the umbilical cord is clamped to stop the flow of blood before it is cut. Clamping the cord can be done right away or it can be done anywhere from 30 seconds to a few minutes after birth.
Waiting to clamp the umbilical cord allows blood to keep flowing to the infant. What are the benefits of delayed umbilical cord clamping in term. New recommendations for newborns nextGroup Recommends Delaying Umbilical Cord Clamping After Healthy DeliveriesLauren Neergard reporting for the AP wrote th.
What Is Delayed Cord Clamping. Delayed cord clamping is the prolongation of the time between the delivery of a newborn and the clamping of the umbilical cord. Delayed umbilical cord clamping is usually performed 25 seconds to 5 minutes after giving birth.
DCC allows more blood to transfer from the placenta to the baby sometimes increasing the childs blood volume by up to a third. The iron in the. As mentioned in American hospitals today umbilical cords are generally cut right away after the baby is born.
So technically speaking delayed cord clamping is when the cord is not cut immediately but rather some time passes first. Well that is a good question. Some providers wait 30 seconds and then pat themselves on the back and make the cut.
To watch them you would think it was the. There are multiple rationales that we have listed that will help you understand why you should delay or not cut the umbilical cord. Babies have a noticeable rise in blood volume as compared to babies whose cords were clamped and cut off without delay.
Many medical bodies say a delay of one to five minutes is optimal. Waiting longer to clamp the cord could reduce the risk of iron deficiency and anaemia particularly in boys. Its a simple technique performed by gently grasping the uncut umbilical cord and squeezing several times from the placenta towards the infant.
In contrast to delayed cord clamping milking provides a placental transfusion without postponing resuscitation and can be completed as quickly as immediate cord clamping. Cutting the Umbilical Cord Throughout your pregnancy the umbilical cord has functioned as the connection between your baby and the placenta. It has brought important nutrients and blood to your baby.
During the late stages of your pregnancy the cord has been passing on antibodies as well benefiting your babys immune system.