Typically the cysts are isolated and can happen in almost any pregnancy. The only association of some significance between an isolated choroid plexus cyst and a possible fetal problem is with trisomy 18.

However in a very small percentage of fetuses with choroid plexus cysts there is an associated chromosome disorder called trisomy 18.
Choroid plexus cyst trisomy 18. Fetuses with trisomy 18 have choroid plexus cysts about a third of the time. Therefore when we see choroid plexus cysts we are concerned that the fetus may have trisomy 18. Trisomy 18 is rare.
It is present in less than 1 in 3000 newborns. Choroid plexus cysts are relatively common in normal fetuses. Trisomy 18 was detected in four patients and one of them had isolated choroid plexus cyst.
The likelihood ratio in cases of isolated choroid plexus cysts for trisomy 18 was 951 95 confidence interval 02-41. According to the study the individual risk for trisomy 18 in isolated choroid plexus cyst should be calculated by using the likelihood ratio. These data allows the physician to express the.
There have been reports associating a choroid plexus cyst with Trisomy 18. Fetuses with trisomy 18 have choroid plexus cysts about one third of the time. In fetuses with choroid plexus cysts 21 have an abnormal number of chromosomes with the majority having other anomalies that.
As mentioned choroid plexus cysts are present in 1 to 2 percent of normal fetuses. However in a very small percentage of fetuses with choroid plexus cysts there is an associated chromosome disorder called trisomy 18. Fetuses with trisomy 18 have an extra copy of chromosome 18.
Frequently fetuses with trisomy 18 are stillborn. In 102 patients isolated choroid plexus cysts and in seven patients additional fetal anomalies supporting trisomy 18 were detected. Trisomy 18 was detected in four patients and one of them had isolated choroid plexus cyst.
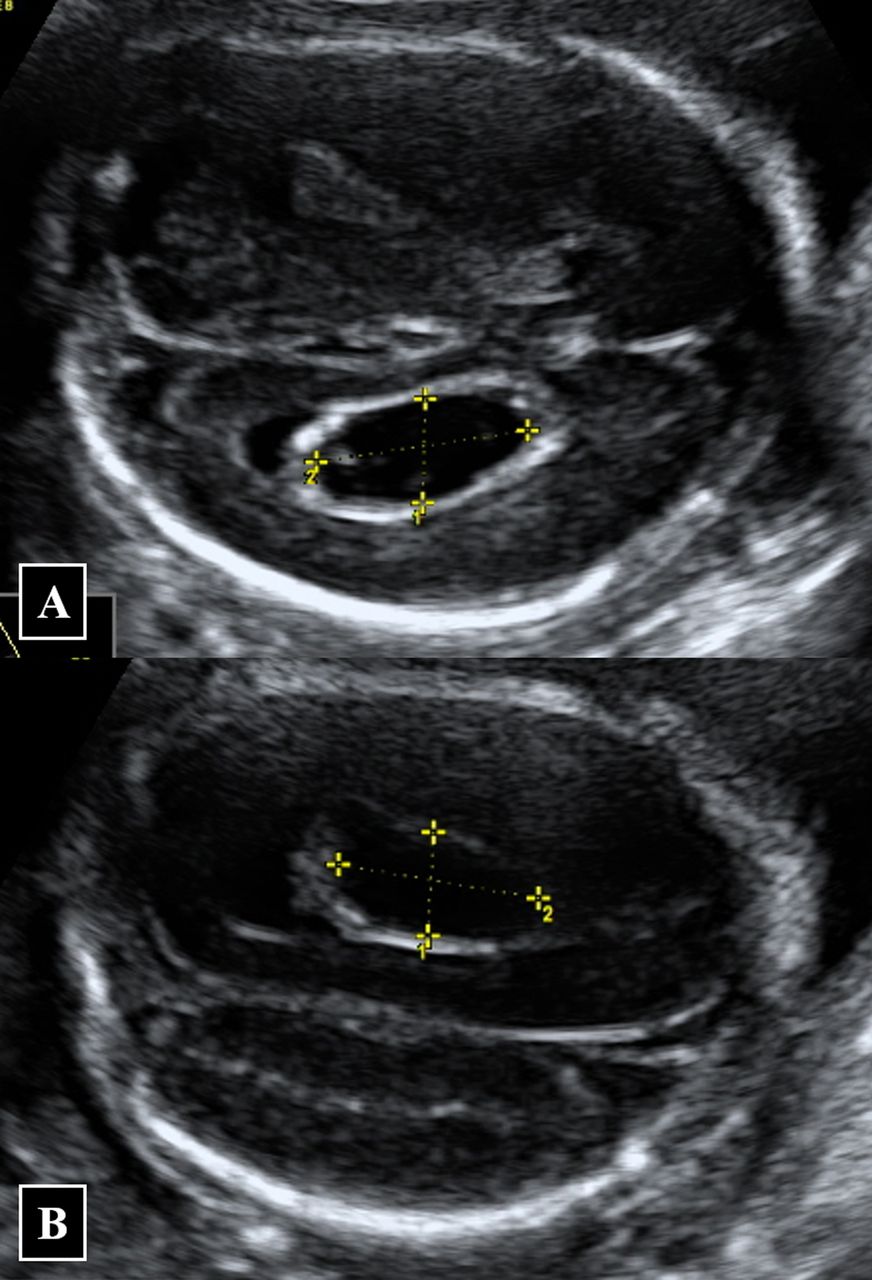
The likelihood ratio in cases of isolated choroid plexus cysts for trisomy 18 was 951 95 confidence interval 0241. According to the study the individual risk for. A CPC is a fluid-filled sac in the choroid plexus part of the brain.
Basically the part that makes fluids. Typically the cysts are isolated and can happen in almost any pregnancy. However these cysts have been correlated with T18.
Trisomy 18 or T18 is also known as Edwards Syndrome. With this genetic disorder many parts of the body are affected. The only association of some significance between an isolated choroid plexus cyst and a possible fetal problem is with trisomy 18.
When a fetus is affected by trisomy 18 multiple structural anomalies are almost always evident including structural heart defects clenched hands talipes deformity of the feet growth restriction and polyhydramnios. Choroid plexus cysts were identified in 109 patients 10910594. In 102 patients isolated choroid plexus cysts and in seven patients additional fetal anomalies supporting trisomy 18 were.
Both of my twins had bilateral choroid plexus cysts at my early anatomy scan at 16 weeks. My MFM told me it is a soft marker for trisomy 18 but my NIPT came back low risk. She said they normally disappear by 20 weeks but sometimes they stay as late as.
Four patients had an abnormality when the choroid plexus cyst was associated with an additional risk factor including two patients with trisomy 18 and one with trisomy 21. An isolated choroid plexus cyst was not associated with a trisomy or other abnormalities in this study. When a choroid plexus cyst was associated with an.
A meta-analysis of 8 studies between 1990 and 2000 with choroid plexus cysts that were identified in second-trimester an incidence of 12. The incidence of the cysts in women younger than 35 was 1 n1017. The study found no cases of trisomy 18 in fetuses with cysts whose mother was younger than 35.
The presence of isolated second-trimester choroid plexus cysts increases the base risk of trisomy 18 by a factor of 709. This likelihood ratio can be multiplied by the risk calculated according to maternal age to obtain the individual risk of trisomy 18 and. Risk of trisomy 18 in a fetus with ultrasonographic diagnosis of choroid plexus cysts and no other anomalies is controversial.
Using our data and current literature we performed a meta-analysis and estimated the positive predictive value of isolated choroid plexus cysts fot risomy 18. It is well accepted that choroid plexus cyst s in association with other congenital anomalies warrant amniocentesis to determine fetal karyotype. The presence of isolated CPC varies around 1 in.
10 of fetuses with trisomy 18 may have choroid plexus cysts as the solitary identifiable indicator on ultrasound. While the number of cysts and the cysts distribution do not alter the risk of aneuploidy it is seen that large cysts with diameter 10 mm may bear a higher risk of aneuploidy and can merit invasive prenatal genetic testing. This paper examines the association between fetal choroid plexus cysts CPCs and trisomy 18 and proposes a method by which risks can be derived taking into.