
Many caregivers routinely wait longer before cutting while others continue the outdated practice of cutting the cord immediately. Deferred cord clamping What is deferred cord clamping.
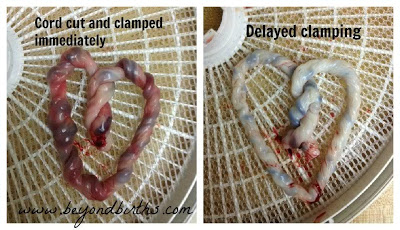
These are some of the benefits of preserving the umbilical cord of your baby.
Benefits of not cutting the umbilical cord. Anzeige Swiss cord blood bank. Bank cord blood in our bank. The most developed cord blood banking offer on the market.
Reason NOT To Cut The Cord 7. The Cord Is A Source Of Oxygen. While the umbilical cord is attached to the baby he or she still receives oxygen which helps to explain how water-birthed babies can breathe while under water.
Its not until they hit the air that the breathing reflex is stimulated. Benefits of delayed cord clamping Delayed cord clamping is considered best practice because of the significant increase in babys blood volume when its used. Delayed cord clamping results in up to 13 more blood volume at birth than in infants whose cord is cut immediately.
Azadeh Ansari 2015 The great umbilical cord-cutting debate. Haelle Tara for NPR 2015 Delayed Umbilical Cord Clamping May Benefit Children Years Later. 2006 Effect of timing of umbilical cord clamping on iron status in Mexican infants.
Dont cut that cord just yet. A research review finds keeping the umbilical cord of a newborn intact a little longer may lead to better health benefits. There has been research in the past few years which found that when doctors delay clamping the cord for three minutes the baby receives higher levels of iron which prevents anemia but beyond that time frame leaving the cord attached to the baby serves no purpose because it no longer feeds nutrients to the baby.
Delayed cord clamping offers the most benefits to preterm infants but it also benefits full-term babies and mothers. A 2013 review linked delayed cord clamping to. These are some of the benefits of preserving the umbilical cord of your baby.
There is no risk involved to the mother or the baby. Extracting stem cells through umbilical cord is a simpler process than extracting it through bone marrow and less painful. Doctors traditionally cut a newborns umbilical cord right after birth but recent research shows that there may be benefits in delayed cord clamping.
In most cases the umbilical cord will be cut following birth. However it does not necessarily have to be cut immediately. According to a review by The Cochrane Library it is possible that keeping your baby connected to their umbilical cord for a period longer than one minute may result in specific health outcomes.
Babies who do not have their cord cut or have a delayed cutting of the cord have seen to have very few or no requirement with transfusions. Babies depend on the umbilical cord while in-utero to provide nutrition but mainly it is their main source of being provided oxygen. Doctors often clamp the umbilical cord right after a baby is born.
But a new study suggests that there might be many benefits and few risks if doctors hold off for at least a minute to allow more. Babies dont experience more jaundice as formerly thought and get the benefit of an immediate oxygen boost from the blood supply in the placenta. Many caregivers routinely wait longer before cutting while others continue the outdated practice of cutting the cord immediately.
Some new studies have found that DCC can have a positive effect on both preterm and full-term babies. These benefits include an increase in placental transfusion a 60 increase of RBCs and a 30 increase in neonatal blood volume. Another advantage of DCC is the decreased risk of iron deficiency anemia.
The cutting of the umbilical cord is the only surgery that every human alive has gone through. Weve all got that weird little scar on our stomachs that mark the spot where we were once. An effective cord-cutting process will usually involve at least 10 steps and will take at least 35-40 minutes.
Effective cord-cutting does not happen through simply asking the archangels to sever the cords seeing them do it and then thanking them. Believe me Ive tried it and it doesnt work. Deferred cord clamping What is deferred cord clamping.
After birth the babys umbilical cord will be clamped and cut separating the baby from the placenta. There is evidence that babies benefit from a delay before clamping the cord allowing time for extra blood to flow from the placenta into the baby. Anzeige Swiss cord blood bank.
Bank cord blood in our bank. The most developed cord blood banking offer on the market.